Only The SEO Elite Get These 30 Critical Technical SEO Points Right
If you’re a marketer, then I bet Technical SEO is intimidating.
The word “technical” alone might remind you of code—an alien language completely unknown to you.
The good news is that as long as you know the right tips and tricks, there’s a chance that you can become a technical SEO elite.
Interested to find out find out what these tips and tricks are? In today’s article, I’ll walk you through you exactly what you need to do.
1. Site Speed Matters
A study by Akamai and Gomez.com found that people expect sites to load by 2 seconds. If a site takes a second too long, then the back button is the inevitable alternative.
With this in mind, you should know your site’s speed.
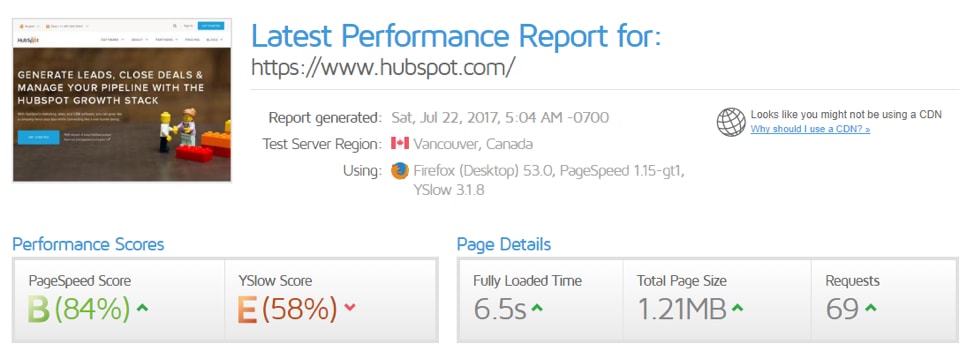
My favorite tool for this task is GTmetrix.
Just copy and paste the URL in the text box.
The results will show the loading time and tips on how you can speed up your site.
2. Know Your Mobile Site Speed
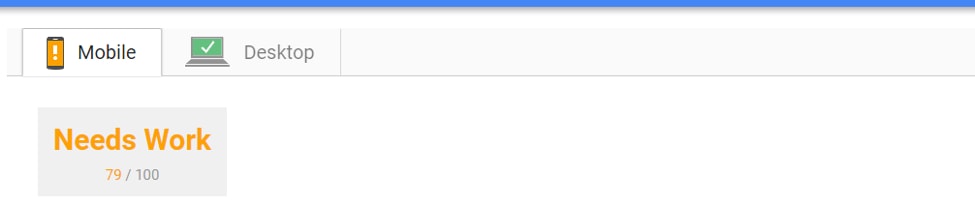
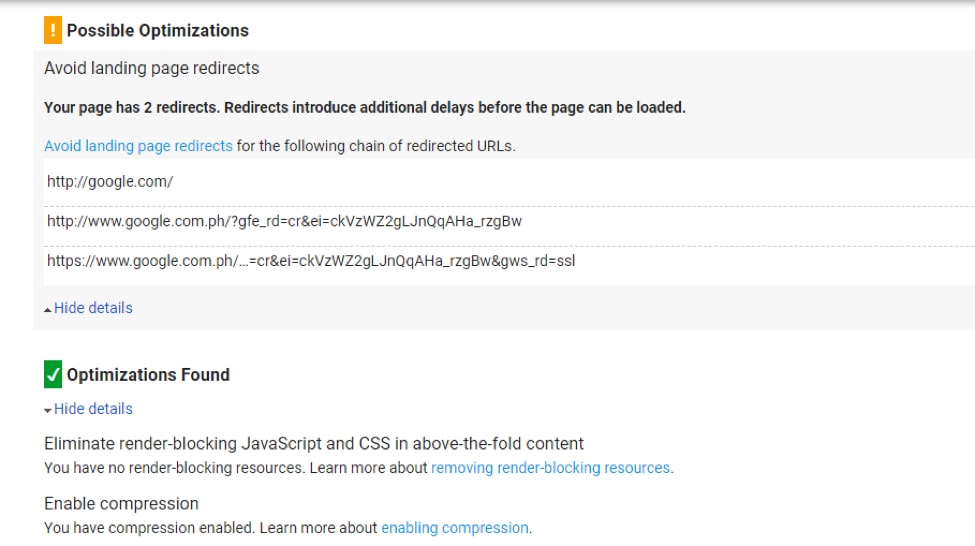
Site speed is different on mobile. So, use Google PageSpeed Insights to determine your mobile site’s speed.
Let’s check the mobile site speed of google.com.au
It’s best to aim for a score above 50. This suggests that your site speed takes 2 seconds or less to load. In contrast, a lower score implies that your site needs more time to load.
When you click the “Show how to fix” link, you are also presented with tips on how to improve your site.
3. Mobile-Friendliness is a Must
There are 4.30 billion mobile phone users.
As a result, if your site isn’t mobile-friendly, then you are missing out on A LOT!
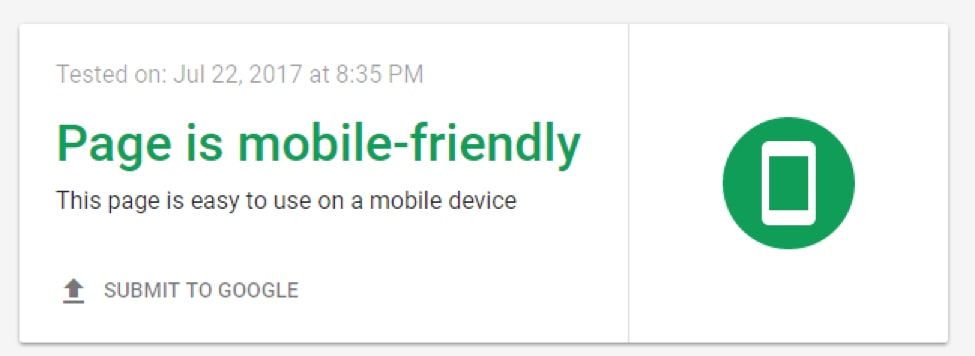
Fortunately, it’s easy to determine your site’s mobile-friendliness with Google’s Mobile Friendly Test. All you need to do is enter your site’s URL.
4. Determine Your Domain Authority
Want to know your site’s domain authority?
No worries! MozBar gets the job done.
After you’ve installed the plugin, just visit a page and click the extension.
The MozBar will reveal your page authority and domain authority.
5. Develop a Responsive Site Design
Nothing’s more frustrating than a site that can’t adjust to your phone’s screen size.
The good news is that it’s easy to make web pages shrink or expand across a variety of screen sizes. Simply set a percentage and abandon the widths.
With the 50% code, the body section will always occupy half of the screen, regardless of the screen size.
6. Compress Images
A picture is worth a thousand words.
But, a picture with a thousand pixels is a big problem.
It takes so much time to load! And, no one’s willing to wait for 20 to 30 seconds to view an image.
The solution?
You can use image compressors to decrease the size of your image. Just upload your images to sites such as Compress JPEG, Tiny JPG or Compressor.io.
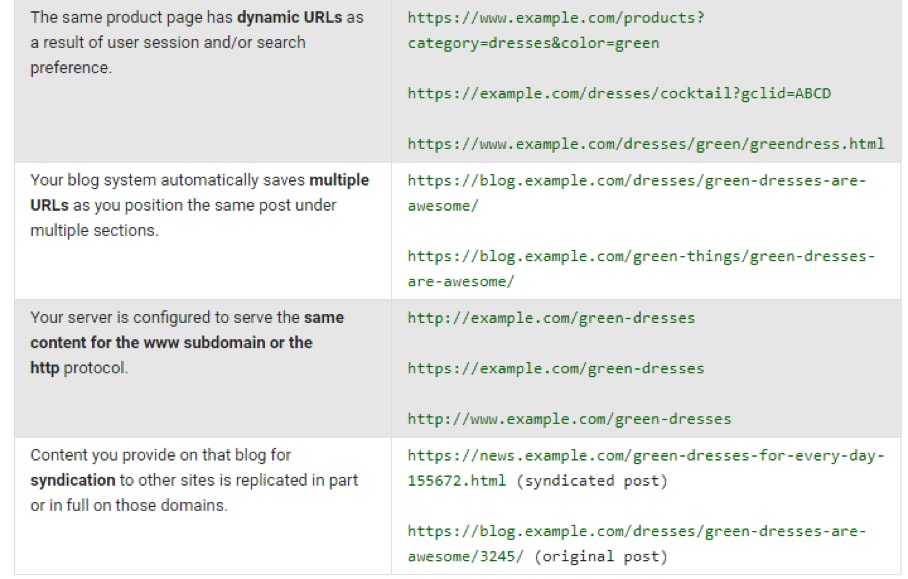
7. Optimize URLs
URL structure can make or break a page.
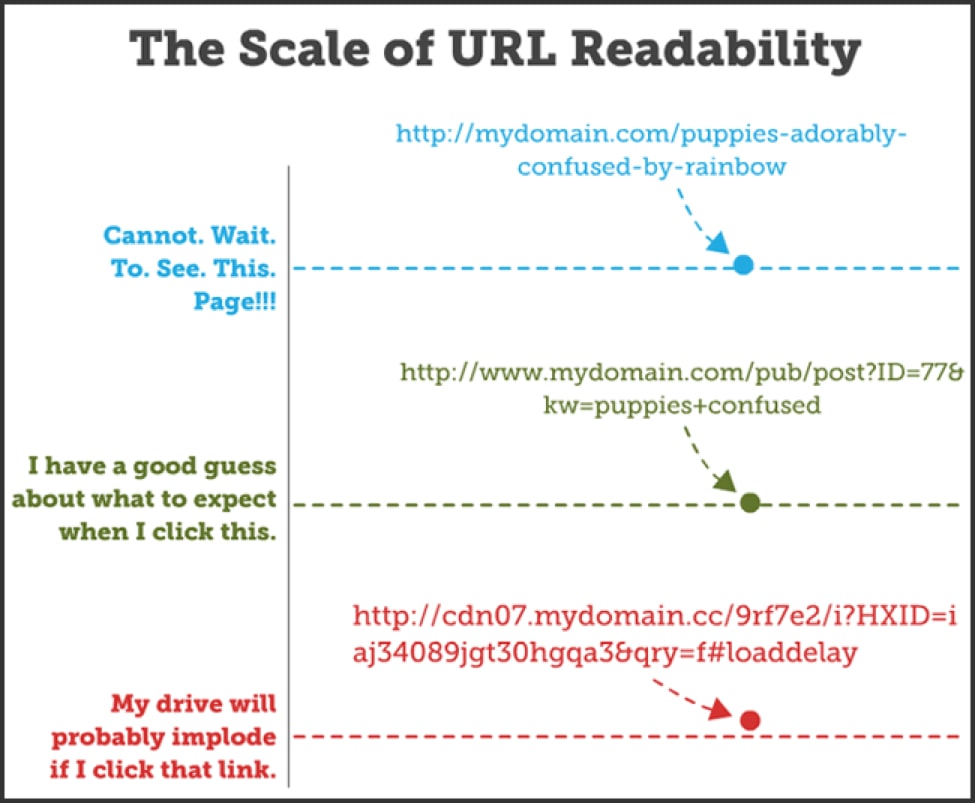
The image below from Moz proves my point.
The first URL has high readability. Users know what page to expect when they click the URL. In contrast, the last URL could be a harmful site in disguise.
So, here’s a few tips to help you improve your URLs:
- Include relevant keywords in the URL structure
- Shoot for 50 – 60 characters
- Avoid extraneous characters (i.e. &, %, $, and @ ).
- Avoid filler words (i.e. a, an, or and but).
- Use a “.com” domain
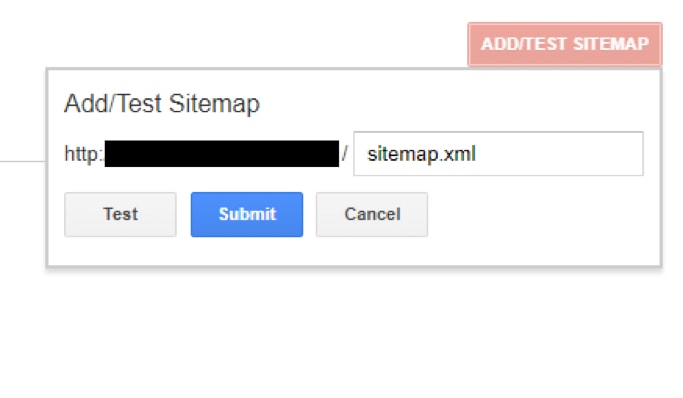
8. Create a Sitemap
A simple site architecture helps your pages get indexed faster and ranked higher.
To create a site architecture, you need a sitemap. This will help search spiders identify pages on your site.
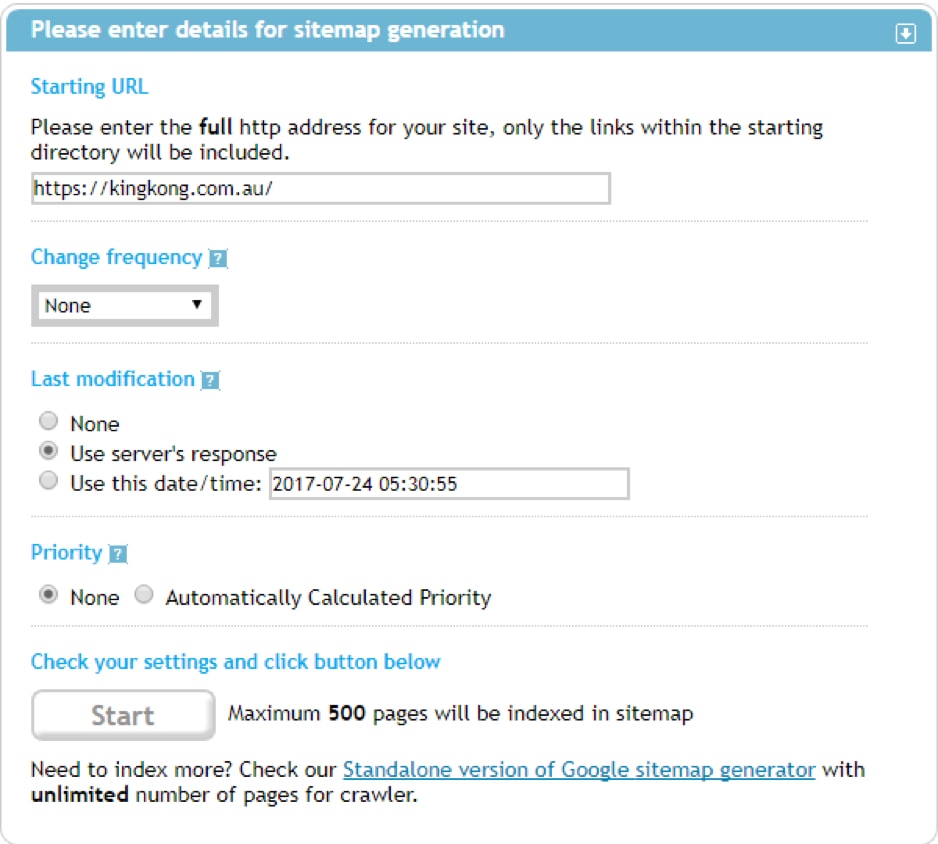
Most experts recommend an XML sitemap, which you can generate at XML-Sitemaps.com.
To get started, indicate the address of your site.
Next, download the sitemap and upload it in the domain root folder of your site.
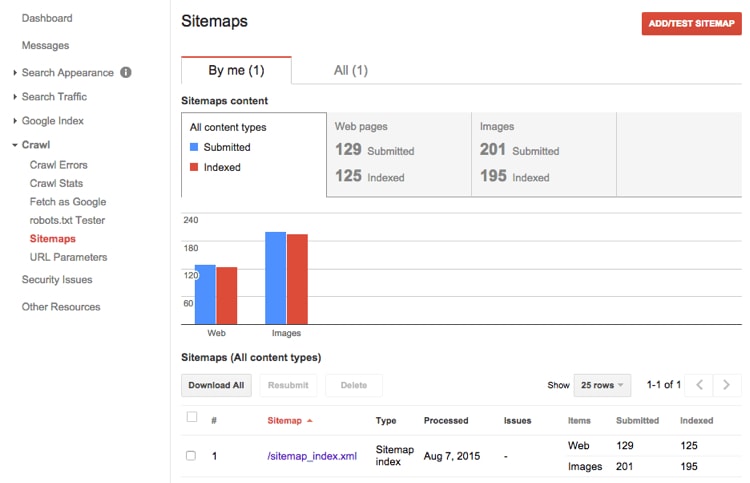
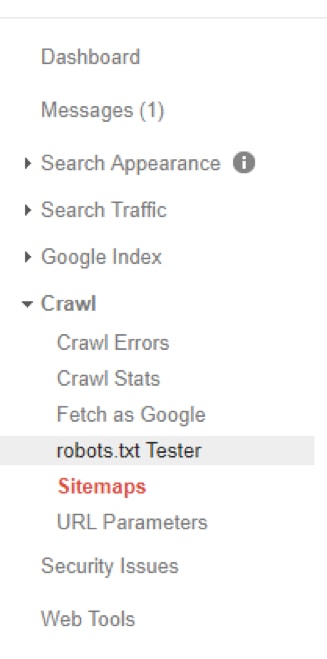
When you’re done, visit your site on the Google Search Console, then go to “Sitemaps”.
Place the significant portion of the URL from XML-sitemaps.com.
Finally, you can refresh the page to see your sitemap data.
9. Improve Your Site Architecture with Silos
Siloing or categorizing your content, is the key to improving your site’s architecture. Here’s an overview of how Hubspot categorizes its blog posts:
- https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/topic/business
- https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/topic/blogging
- https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/topic/content-marketing
When visitors click the link, they can view recent content published in that category.
Siloing also enables users to add faceted navigation or filter results.
Since Google’s main objective is to generate the most relevant results, siloing helps search engines pinpoint the post’s topic and increase your site traffic.
10. Identify Duplicated Content
Some pages can be accessed via multiple URLs.
According to Google Support, here are the reasons why this happens:
Duplicated content isn’t an instant deal breaker. But, it’s problematic because:
- It confuses search engines
- It makes it difficult to combine tracking metrics for a specific page.
- It makes it difficult to increase traffic in your preferred URL.
- Google’s “phantom” update gives lower rankings to sites with duplicated content.
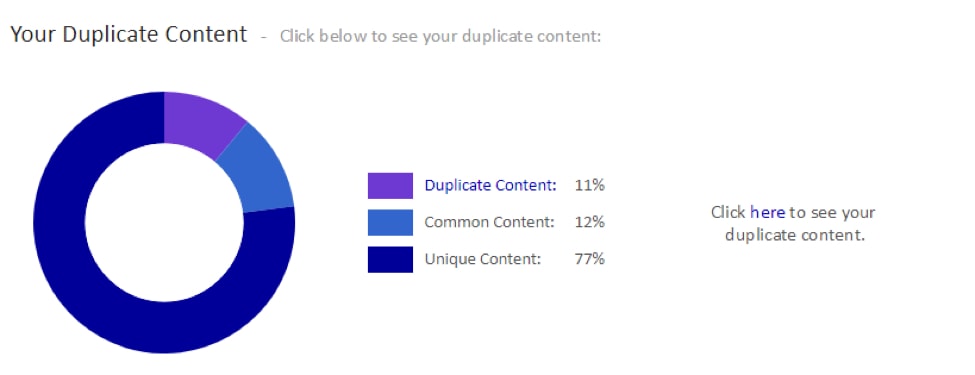
Fortunately, you can use Siteliner to easily find duplicated content.
Scroll down to the “Duplicate Content” section
Click the “here” link to show duplicated pages.
11. Use Canonical Tags
You can also fix duplicate content issues by adding a canonical link.
The rel=”canonical” link element lets Google know the preferred URL to use to access the page.
Here’s an example:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://blog.example.com/jeans/jeans-sale” />
The presence of the tag increases the likelihood that Google will direct users to the preferred URL indicated.
12. Create a Custom 404 Page
If you reached a dead end, then which page will get you to go back to the site.
Is it this?
Or this?
The answer seems obvious, so I’ll let you decide.
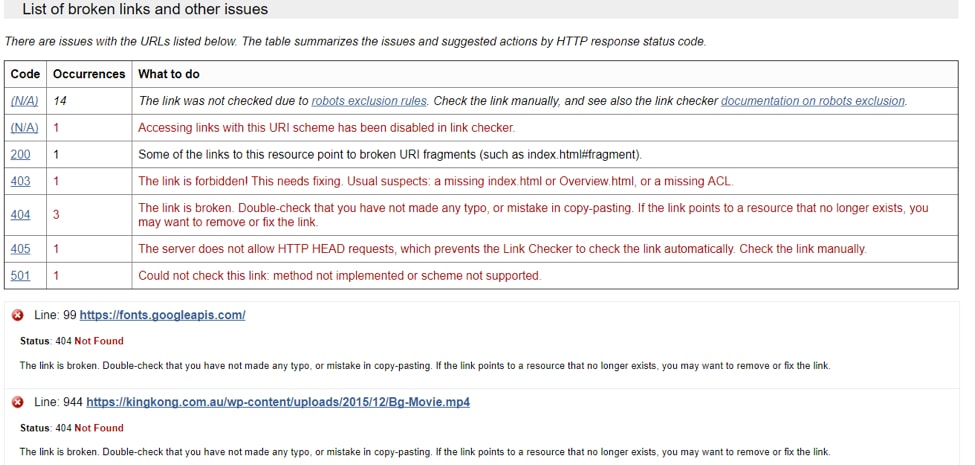
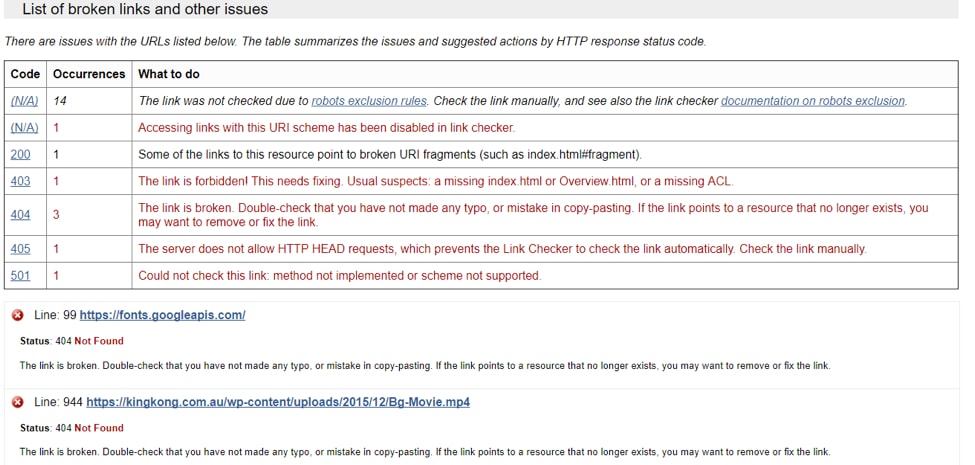
13. Get Rid of Broken Links
Broken links are a big NO!
They’re a guaranteed turn off for site users and Google.
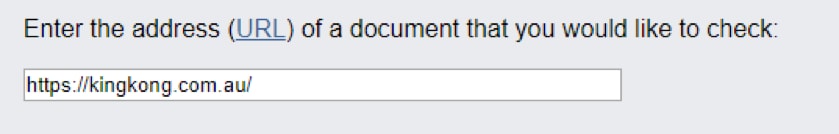
To check whether a site your site has them, use the W3C Broken Link tool.
Simply, enter the URL of your site and you’ll be presented with a list of broken links and other issues.
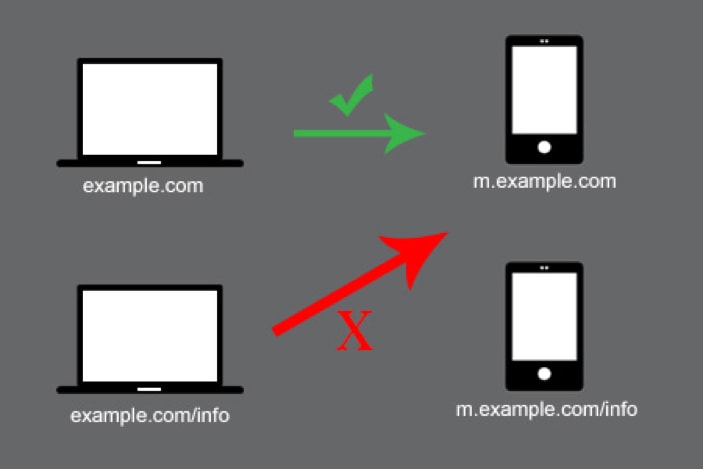
14. Avoid Faulty Redirects
Having separate URLs for a mobile and desktop site can cause big problems.
Desktop users might be redirected to a page on the mobile site. Or, the other way around.
This is faulty redirects in a nutshell.
It’s also a big deal on mobile. Why? Let’s say, you’re using a phone and the web pages aren’t formatted to fit your small screen. You would be forced to scroll left and right just to see the text or immediately leave the site.
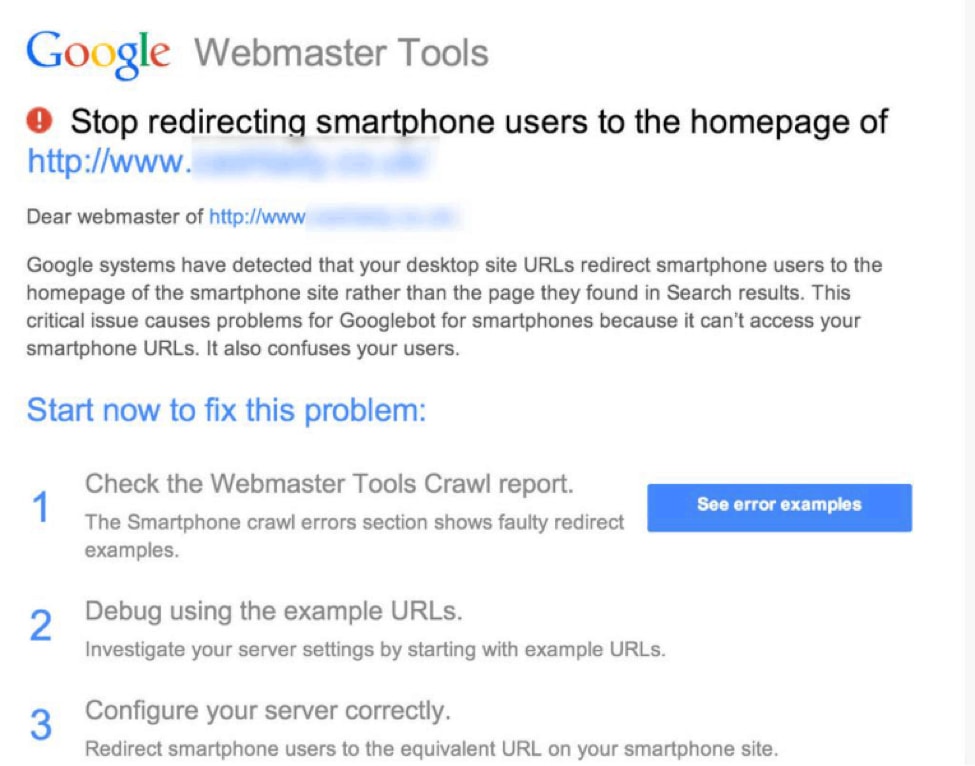
(source)
Thanks to Google Webmasters, it’s easy to avoid this problem. The site notifies website users via email when their sites have faulty redirects.
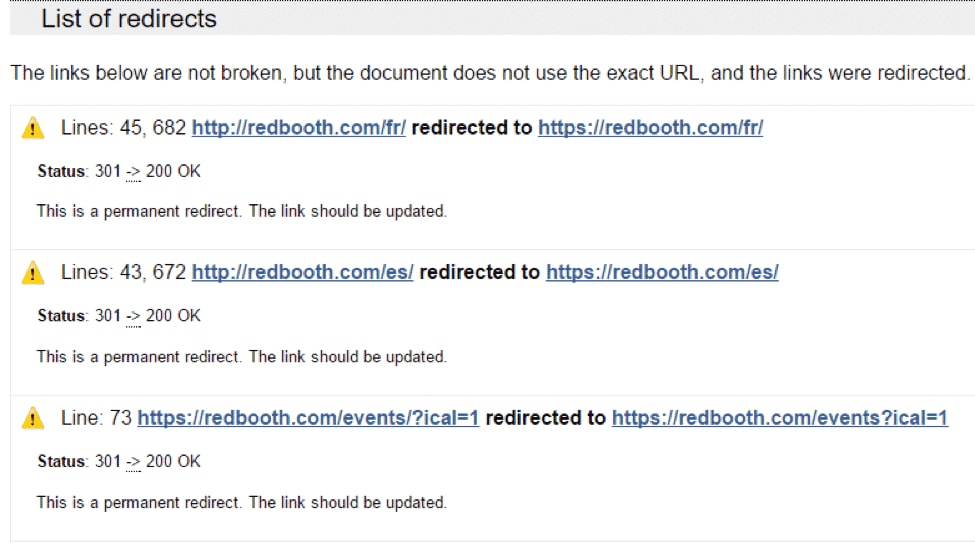
15. Minimize Redirects
Redirects aren’t always a deal-breaker. But, they can slow down site speed.
After all, when you visit the page, the computer has to load that page, redirect you and load another page.
So, how do you spot and stop redirects?
The W3C Broken Link tool is the right tool for the job. Just enter the site’s URL and it will display a list of redirects.
16. Use 301 Redirects, not 302
Redirects have two basic types:
- 301: a permanent redirect
- 302: a temporary redirect
A 301 redirect suggests that the page has been permanently moved to another URL. It’s a crowd favorite since it transfers 90-99% of link juice (ranking power) to the redirected page.
In contrast, a 302 redirect suggests that the redirected page is only temporary, so the link juice isn’t transferred.
To check the type of redirects in your page, you can use Redirect Path.
After you’ve installed the plugin, browse your site. The plugin lets you know if you reached a page via a 301 or 302 redirect.
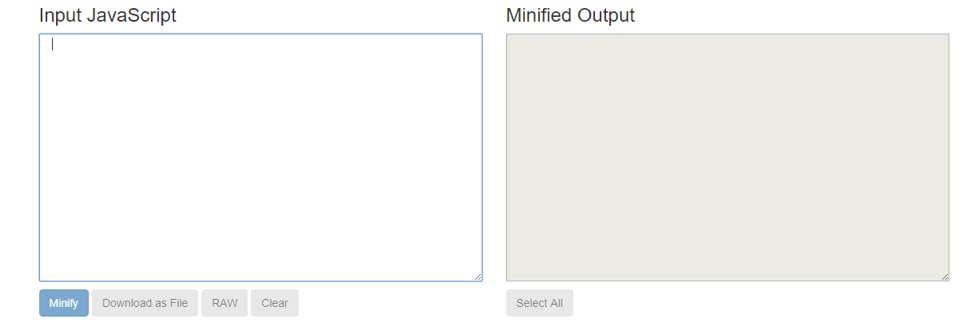
17. Minify Codes
Most developers add unnecessary characters, spacing and comments to make their codes readable. While it allows them to understand their codes, it can put a strain on site speed.
After all, more characters require computers to allot more time to read the code.
On the bright side, it’s easy to minify codes with Javascript Minifier.
Just paste your Javascript code on the left box and copy the minified code on the right box.
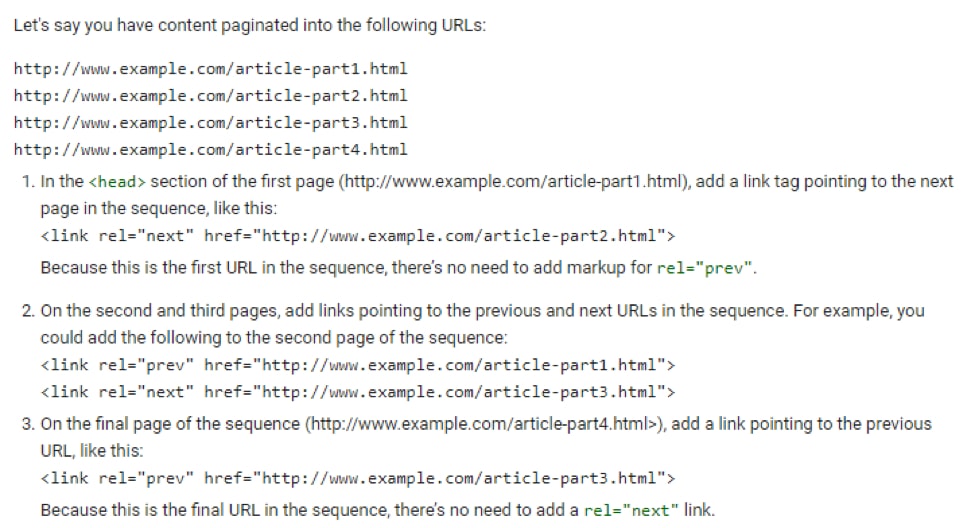
18. Keep Pagination in Mind
Pagination lets Google know which pages or URLs belong to a series. If you have a blog post with a series of pages, then pagination lets Google know the relationships between these URLs.
It also helps Google index content and determine the page where it should direct users first (usually page # 1).
Here’s how these codes are added according to Google Support:
19. Use Language Meta Tags
Does your site come in a variety of different languages?
If it does, then don’t forget to add a language tag. This helps search engines easily determine the site’s country version.
Here’s how the tag appears in a German site:
<meta http-equiv=”Content-Language” content=”de-DE” />
Note that the code must be placed in every page of the site’s German version.
While it might not result in a huge increase in traffic, it can boost your rank on local search engines.
20. Never Forget HREFLANG tags
Besides the language tag, you also need to place the HREFLANG tags on sites with different language versions.
If your site sells products in America, Japan and Portugal, then the tags might look like this:
The second example tells Google the Japanese equivalent of your site, in a Google Japan search engine.
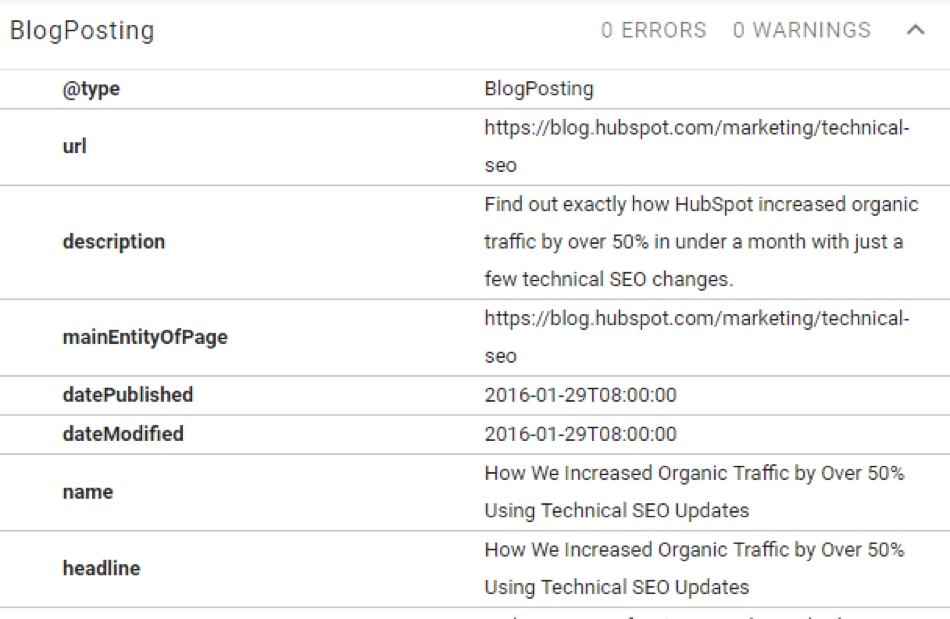
21. Use Blog Schema Markups
How do you make Google understand the individual elements of your blog content?
The answer lies in Schema markups.
For starters, Schema helps search engines break down your blog post through a variety of categories, such as:
Here’s an overview of Schemas in action in a Hubspot blog post:
While Schema won’t skyrocket the blog post’s traffic, it helps Google make decisions on how your post will be displayed.
Not a coder? No worries.
Marketers with no coding experience can manage Schema markup with the Schema app. Once installed, all you need to do is type the text in the specified Schema fields. You can also manually edit these fields yourself.
22. Know the Status of Your Site
If you want to get ahead, then you have to know your ranking.
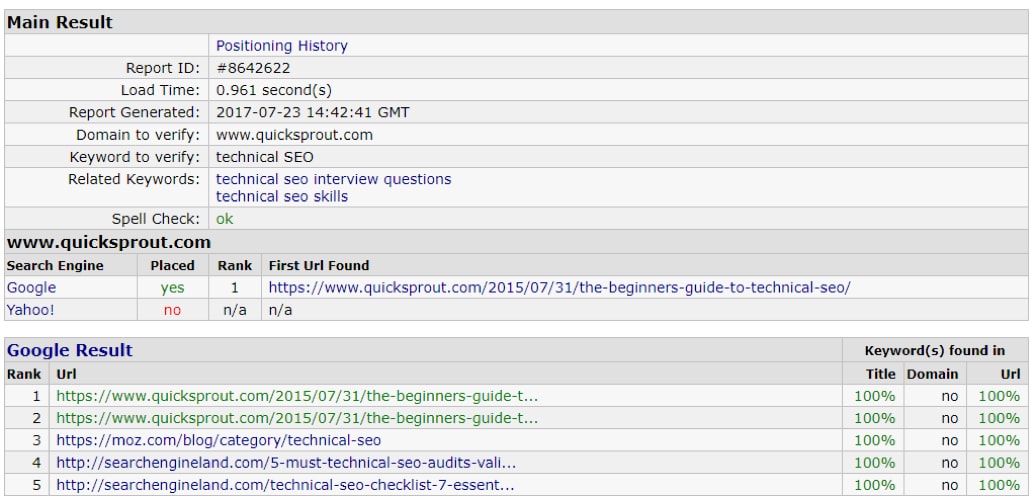
This is why I regularly use SEO Centro to determine a site’s ranking for a target keyword.
In the image below, I used the tool to determine the ranking of Quicksprout for the keyword technical SEO.
The results found that Quicksprout ranked #1 and #2 on Google. Additionally, the keywords related to technical SEO are: technical SEO interview questions and technical SEO skills.
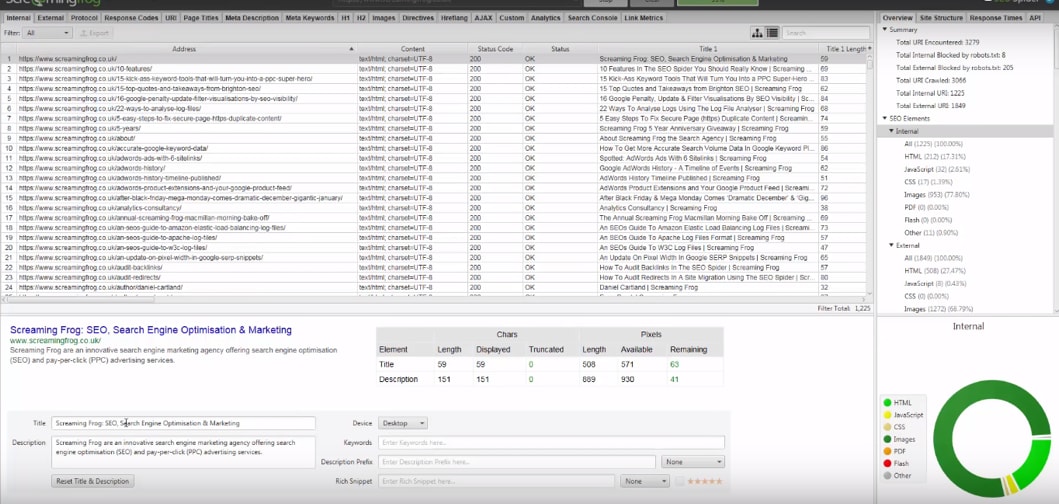
23. Crawl Your Website with Screaming Frog
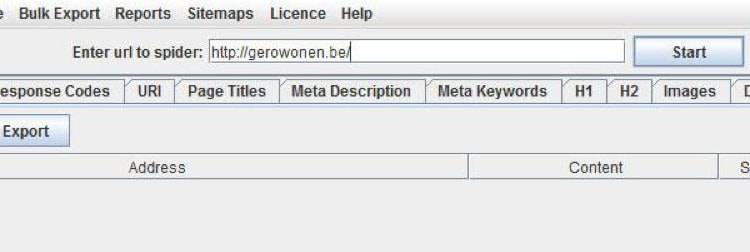
Regularly use Screaming Frog to crawl your site and determine its issues.
You can easily download the free application on the website.
After installation, then enter your site’s URL.
You will then see a TON of data!
Here’s a list of information that can be generated from Screaming Frog from Neil Patel:
24. Improve Website Navigation with Internal Links
Here’s the deal:
It should only take three clicks for users to find information.
This sacred rule becomes a lot harder to follow as your website grows. As your site’s page count increases, then your site architecture becomes a lot more complex.
The solution? Internal links.
For starters, internal links work by linking keywords in your blog post, to another page or post on your website.
Usually site owners link keywords from their new content, to their old content. However, only a few link link keywords from old content to new content.
Give the opposite a try.
It might work wonders on your site’s architecture.
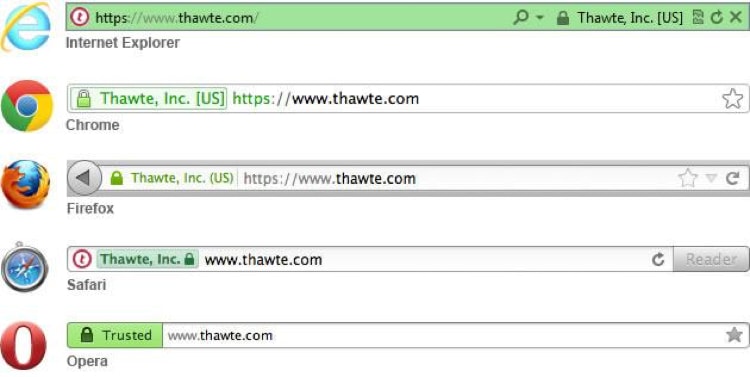
25. Migrate from HTTP to HTTPS
Online security is a big deal these days.
Since cybercrime cost the global economy $450 billion in 2017, search engines rank secure connections first.
As a result, the migration from HTTP to HTTPS is the new trend.
For starters, HTTPS stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). It is the secure version of HTTP. It also comes with an SSL certificate combined with a key needed to initiate the secure session.
Here’s how HTTPS connections look like:
(Source)
You can buy an SSL certificate from Namecheap. This is a MUST, especially if your site deals with shopping orders and online transactions.
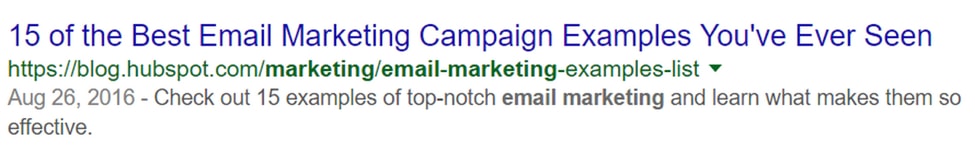
26. Include Relevant Keywords in Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
When you see search engine results, you don’t immediately click the first link that you find.
I bet you assess whether the title and the meta descriptions contain relevant keywords. This is why keywords are important. If your title and description don’t contain the right target keywords, then visitors will ignore it.
Let’s take a look at the title and page description of a Hubspot blog post. The title contains the main target keyword “email marketing campaigns” and the meta description contains the keyword variation “top-notch email marketing”.
27. Caching Plugins
Some plugins can improve your site’s performance and help you reach some goals. Here are some examples:
P3Profiler – used to determine how plugins impact site speed.
WPOptimize – helps you remove unnecessary data including spam comments, trash items and plugin data.
Akismet – determines whether comments are spam.
28. Don’t Overuse Plugins
Plugins are great. But, too much can damage your site’s speed.
As a result, you need to limit the number of plugins you use. In addition, read reviews about the plugin, before installation.
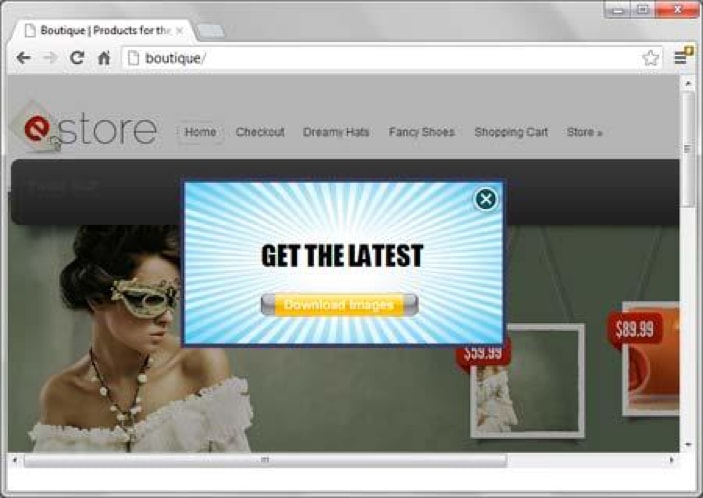
29. Avoid Intrusive Interstitial Popups
Intrusive interstitials are popup ads.
Not surprisingly, they’re deal-breakers for SEO.
While these ads are bearable on laptops or PCs, they’re frustrating on mobile. They’re extremely difficult to close, so the back button is the inevitable alternative.
(Source)
30. Upload HTML 5 Videos and Avoid Flash
Uploaded a video but it won’t play on mobile? Yikes.
You might have uploaded a Flash video, instead of an HTML 5.
As of 2012, Google’s Android has dropped its support for Adobe Flashplayer.
Conclusion
It’s important is to remember these points when improving your technical SEO strategy. If you stay on track, you’ll soon see slow but steady improvements on your site’s SEO ranking.
Got any more points for technical SEO? Let me know in the comments!











Hey!
It looks like you're browsing in . Would you like to switch over to the website?